Knee osteoarthritis is so common that it has a different name: gonarthrosis. Another name for this disease is osteoarthritis deformans.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint worries 20% of the population, its ICD-10 code is M17. Half of knee pathologies are due to osteoarthritis. This is a disease in which the cartilage tissue and joint surface degenerate: they disintegrate. The joint receives few nutrients and oxygen, its function deteriorates and inflammation occurs. It becomes inactive and hurts, the patient's quality of life decreases. Complications of osteoarthritis lead to a wheelchair.
Let's find out what osteoarthritis of the knee joint is and how to treat it. How can the disease be prevented and how dangerous is it?
Causes and classification
The causes of osteoarthritis of the knee joint are different: mechanical damage, hereditary predisposition, metabolic disorders.
The onset of the disease is associated with excessive stress on the knees. This is a work injury in many sports. People with a high degree of obesity, over 60 years of age, almost always present osteoarthritis of one degree or another due to constant microtrauma. Osteoarthritis refers to occupational diseases in areas where a person has to stand or lift heavy objects for a long time. The disease may begin after rheumatoid arthritis.
The most common cause of knee osteoarthritis is an injury. The second most common is dysplasia in childhood. Inflammation due to autoimmune pathologies is the third source of osteoarthritis. Generally there are several reasons, one complements the other.
The types of osteoarthritis of the knee joint are divided according to the causes into primary and secondary. If the etiology is unknown, primary osteoarthritis is diagnosed; If the cause is determined, secondary osteoarthritis is diagnosed.
Development mechanism
Cartilage is nourished due to constant changes in osmotic pressure. When the joint is loaded, the viscosity of the intra-articular fluid decreases and its quantity increases. In a calm state, the intra-articular fluid becomes viscous and its quantity decreases. Normally, these processes alternate. The cartilage plate, acting as a pump, when loaded, pushes fluid out of the joint, and when relaxed, it sucks it in. This is how the joint tissues are nourished. The pathological process manifests itself if the joint is exposed to destructive influences:
- If the load is great and the joint does not have time to recover, nutrition is disturbed. The cartilage thins, cracks and ulcers appear;
- The structure of collagen fibers is altered and they are absorbed less well. The cartilage and kneecap soften, become inelastic and their functions worsen;
- Bone growths appear in the joint. The membrane of the joint capsule becomes irritated and inflamed;
- As a person begins to take care of their knee and move little, less intra-articular fluid is produced. The cartilage surface becomes dry and rough;
- The knee receives even less nutrition, atrophies and its destruction accelerates.
Signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint appear: it becomes inactive and pain occurs. The pain is especially intense in the morning and after prolonged immobility.
Stages of osteoarthritis
There are three degrees of osteoarthritis:
- Initial stage. The tissues have not yet been destroyed. So far, only the function of the synovial membrane is deteriorating. The composition of the intra-articular fluid has changed. The knee can no longer bear normal load;
- The articular cartilage and menisci begin to deteriorate. Osteophytes (bone formations) grow on bones. Inflammation and pain appear;
- Difficult stage. The supporting platform of the knee joint is deformed and the axis of the leg changes. The ligaments shorten and the joint capsule becomes stiff. The joint is pathologically mobile, but it is impossible to completely bend or straighten it. Inflammation and pain are pronounced.
On a note!
At the beginning of the disease, the muscles are intact. Its function is gradually lost. In the third stage, movement is very limited. Due to a change in the axis of motion, the insertion sites of the muscles change. The muscles are deformed: they contract or stretch, they can no longer contract normally. The nutrition of all leg tissues is affected.
Symptoms
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint at the beginning of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way and do not force the patient to consult a doctor. The patient notices fatigue and pain, but does not give them much importance.
The classic sign of knee osteoarthritis is immobility and stiffness in the joint, a pulling sensation in the popliteal region, and pain after exercise. It is difficult to move in the morning or after a long period of immobility. Relief comes after the patient stretches the knee, massages it and walks.
After a while, the intensity and duration of the pain increase. A crunch appears in the joint, it stops bending and flexing completely. A person begins to limp when walking; Most patients go to the doctor with this complaint. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint usually begins only in the second stage.
If nothing is done, movement will only be possible with outside help. When the patient lies down, the knee hurts less, but the pain usually bothers at night.
In the second and third stages, the knee joint is deformed: the contours of the bones are clearly outlined, and the lower leg is curved. If you put your hand on your knee, you will hear a creaking sound as it bends and straightens. When the kneecap moves, it also creaks. Fluid accumulates in the socket, the joint swells and the tissues bulge.
As the disease progresses, all symptoms become more pronounced.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee joint is carried out comprehensively: an anamnesis is collected, instrumental and laboratory methods are prescribed.
Inspection
The doctor examines the damaged joint, measures the bones and the angle of flexion, and determines the degree of mobility of the joints at an angle.
Analysis
The patient is sent for a general blood test, a biochemical blood test and a general urine test.
bone scan
An x-ray of the knee joint is the main source of information for making a diagnosis. In the photo you see arthrosis of the knee joint: the joint space is narrowed, the cartilage is sclerotic, the bones are damaged; there is joint deformation, salt deposition and dystrophic changes. Osteophytes are clearly visible in the image.
Good to know!
For osteoarthritis of traumatic origin, x-rays have great diagnostic value and should be performed.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnosis is an informative method. Ultrasound does not replace X-rays and does not provide a picture of the nature of the destructive process in the joint.
magnetic resonance
MRI provides a complete picture of the disease. This is a modern and accurate research method that allows you to make a diagnosis at an early stage. The disadvantage of MRI is its high cost.
Treatment
Treatment of the knee joint with osteoarthritis is carried out on an outpatient basis, hospitalization is not required.
Treatment regimen:
- Reduce the load as much as possible;
- Respect the prescribed traffic mode;
- Perform therapeutic exercises.
The goal of treatment is to slow the destruction process, prevent contractures (the inability to fully bend and straighten the leg), and restore joint function if possible. During the rehabilitation period, stay in sanatoriums and resorts shows good results.

Drugs
Only the doctor decides how to treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint. You cannot select medications on your own.
The inflammation is relieved with NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Good to know!
Since arthritis causes severe pain, NSAID injections provide a quick effect and a feeling of relief.
Modern treatment of knee osteoarthritis involves the use of NSAIDs from another group. Its effect is more pronounced.
If there is inflammation of the joint lining, the doctor prescribes corticosteroid hormones for intra-articular administration. Hydrocortisone, Kenalog, Diprospan relieve inflammation and pain, but have many contraindications.
If necessary, antienzymatic substances are injected into the joint cavity: contrical, ovamine, gordox. They can significantly slow down the destructive process.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid and its preparations are also prescribed. Restores the protective and cushioning properties of synovial fluid.
Chondroprotectors are often prescribed, but there is no evidence that they help.
Physiotherapy
The newest methods of treating knee osteoarthritis do not exclude proper loading. The goal of physical therapy is to provide the necessary amount of movement, but not overload the joint, maintaining balance. If the patient does not understand how to treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint, when it is necessary to simultaneously protect the knee and develop it, the result of other methods is sharply reduced or reduced to zero. It is possible to get rid of the disease if the patient is conscious.
Laser therapy and physiotherapy.
Laser treatment and physiotherapy procedures have proven to be excellent, especially if they were able to start from the first stage.
Other methods
Intraosseous blocks provide a therapeutic effect, breaking the cycle of inflammation. Along with the block, multichannel electromyostimulation is used using a special device.
Compresses made with homemade ointments and massages can relieve pain and swelling.
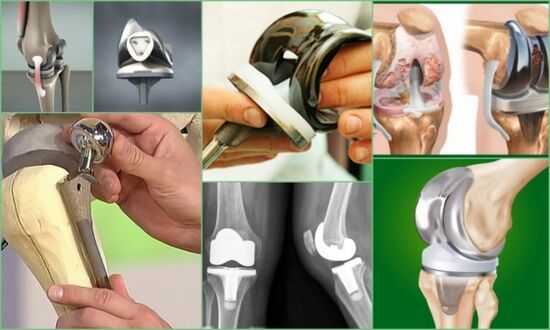
Prosthesis
If necessary, an operation is performed: a knee joint endoprosthesis is placed in the patient. Modern prosthetic methods allow patients to return to sports.
Alternative and traditional medicine.
Proponents of this unconventional approach argue that it is possible to eliminate symptoms and treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint only with their methods, without resorting to medications. This is kinesitherapy (a special set of exercises), ozone therapy (physiotherapy with ozone, which is injected into the joint), homeopathy, treatment with dietary supplements, manual therapy, massage.
Attention!
When using unconventional methods, it should be remembered that their effectiveness has not been proven.
There are original treatment methods, but reviews about them vary.
Rehabilitation and prevention
Only therapeutic exercises and measured load on the joint can restore the osteoarthritis knee joint. If the patient follows all the doctor's recommendations and is ready to fight for his health by all means, in most cases the answer to the question "can osteoarthritis of the knee joint be cured? " is positive. .
Prevention consists of timely care for injuries, active movement without overload, and maintenance of an optimal body mass index.
Patient opinions
Reviews of patients who have undergone traditional treatment are usually positive, but there are also negative ones.
When making a final decision on treatment, you should consult your doctor without forming an opinion based on reviews.
Medicine has learned to successfully treat joint diseases, the consequences of which in the last century inevitably led to disability. In case of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, it is important to seek help in time to determine the stage of the disease and the extent of treatment.






















